Exploring Skin Tone, Skin Shades, and the Role of Genes 101
Skin tone and shades are fascinating aspects of human diversity. They play a significant role in our identity and cultural perceptions. From fair to dark, skin tones vary across different populations and individuals. This article aims to explore skin tone, explore the various skin shades, and understand the role of genes in determining skin color.
Exploring Skin Tone: A Reflection of Diversity
The skin color is resolute by the amount of melanin that is produced by the melanocytes, which is responsible for the skin’s coloring. Melanin is a pigment that is created by these specialized cells, and the more the amount of melanin existing in the skin, the deeper the skin shade. Skin shade is precious by hereditary factors, ecological factors, and evolutionary modifications.
Factors Influencing Skin Tone
Several factors contribute to the wide range of skin tones observed in human populations:
- Genetics: The genetic makeup is accountable for deciding the quantity and kind of pigment generated in the epidermis. Distinct genetic compositions lead to diverse complexions.
- Melanin Production: Melanocytes produce two types of melanin: eumelanin, which gives a brown color, and pheomelanin, which imparts a reddish-yellow hue. The relative proportions of these pigments determine the skin tone.
- Sun Exposure: The sun’s ultraviolet (UV) rays impact the production of melanin. Lengthy exposure to the sun’s radiation triggers melanocytes to generate additional melanin, which leads to a deepened skin tone.
- Geographic Location: Communities residing near the equator frequently exhibit darker complexion, as it affords an enhanced safeguard against detrimental UV radiation. Conversely, populations dwelling in regions with higher latitudes possess lighter skin to enhance the production of vitamin D in areas with inadequate sunlight.
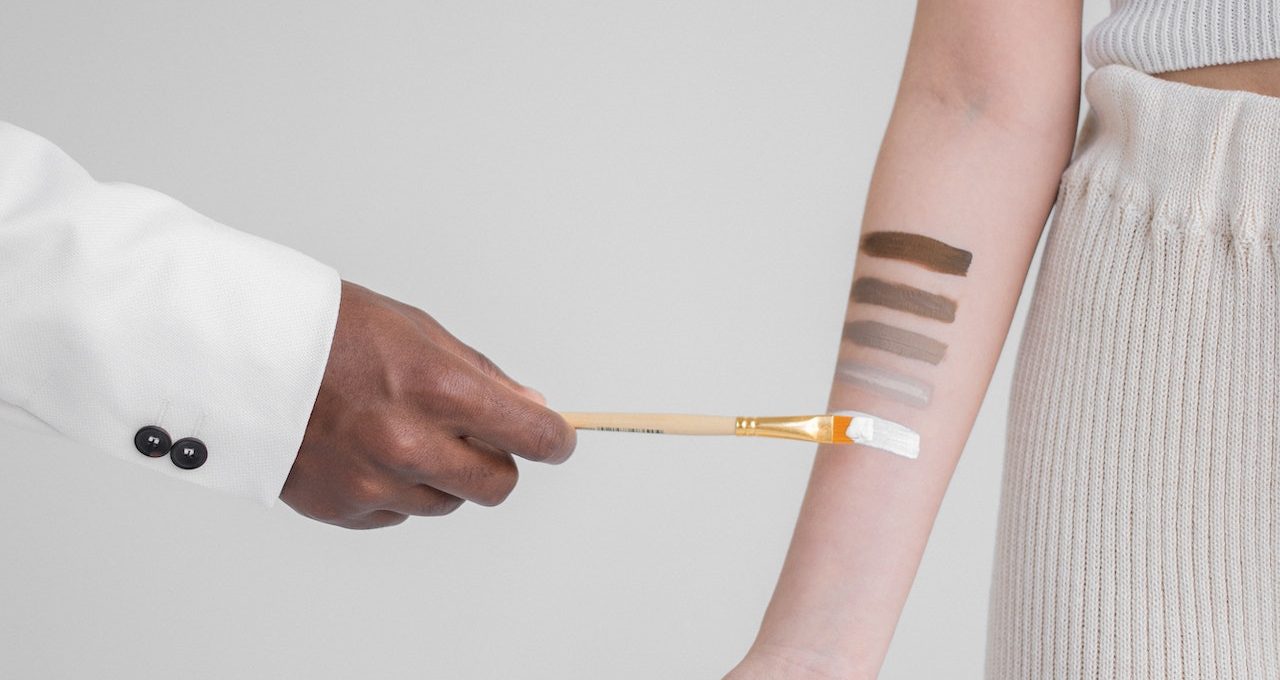
Skin Shades: A Spectrum of Beauty
Human skin shades encompass a vast range, each with its unique beauty and characteristics. Let’s explore some of the common skin shades found worldwide:
1. Fair Skin
Fair skin is commonly associated with lighter tones that tend to burn easily in the sun. Individuals who possess a light complexion frequently exhibit lower levels of melanin and are at a higher risk of experiencing sunburns and harm from the sun’s rays. This specific skin tone is common in areas with limited exposure to sunlight.
2. Olive Skin
An olive skin tone refers to a warm, subtle to moderate complexion with hints of green or yellow undertones. This type of skin tone is commonly found in ethnicities originating from the Mediterranean, the Middle East, and some parts of South Asia. Those with an olive complexion can easily develop a tan and are less likely to experience sunburn.
3. Medium Skin
Medium skin tones encompass a broad range, from warm caramel shades to cooler and neutral undertones. This skin shade is prevalent in diverse populations, including those from Africa, East Asia, and South America.
4. Dark Skin
Dark skin tones are characterized by deep brown to ebony shades. Individuals with darker complexion possess elevated amounts of melanin, providing greater defense against UV radiation. This skin tone is prevalent among communities hailing from sub-Saharan Africa, Southeast Asia, and the Caribbean.
The Role of Genes: Unraveling the Genetic Influence
Genes play a crucial role in defining an individual’s skin tone. Numerous genes are involved, and differences in these genes contribute to the wide range of skin shades observed in different populations.
1. MC1R Gene
The MC1R gene plays a vital role in determining skin and hair color. Variants of this gene can result in different shades of skin. People with variations in MC1R may have fair skin, red hair, and freckles.
2. SLC24A5 Gene
The SLC24A5 gene is responsible for producing a protein that influences melanin production. Variations in this gene are associated with lighter skin tones, particularly in populations of European descent.
3. TYR Gene
The TYR gene plays a role in the generation of an enzyme known as tyrosinase, which is indispensable for the synthesis of melanin. Variations in this gene can cause disorders such as albinism, in which people possess minimal or no melanin, resulting in exceptionally light skin.
4. OCA2 Gene
The OCA2 gene controls the synthesis of melanin in the iris, dermis, and hair. Alterations in this gene are linked to various complexions, such as light, moderate, and deep.
FAQs about Skin Tone, Skin Shades, and Genetics
Q1. Is skin color solely determined by genetics?
Even though genetics play a significant role in deciding skin tone, other factors like exposure to the sun and environmental conditions can also affect the skin’s appearance.
Q2. Can skin tone change over time?
Certainly, complexion may alter as a result of aspects such as exposure to sunlight, the passing of time, shifts in hormones, and some medical ailments. Nevertheless, inherited elements primarily establish the original skin tone.
Q3. Why do people from different ethnic backgrounds have distinct skin shades?
The variation in skin shades among different ethnic backgrounds is primarily a result of genetic adaptations to local environments, such as UV radiation levels.
Q4. Can two parents with light skin have a child with dark skin?
Yes, it is possible. The inheritance of skin tone involves complex interactions between various genes, and even parents with lighter skin can carry genetic variations that lead to darker skin in their offspring.
Q5. Are there health implications associated with specific skin tones?
Although skin complexion does not exclusively determine one’s overall well-being, people with fair skin tones tend to be more vulnerable to sunburn and skin injuries, whereas individuals with darker skin tones have a reduced chance of developing skin cancer but might encounter difficulties in producing sufficient vitamin D in areas with inadequate exposure to sunlight.
Q6. Can skincare routines and lifestyle choices influence skin tone?
A6. Skincare routines, sun protection measures, and lifestyle choices like diet and exercise can help maintain and improve the overall health and appearance of the skin but have a limited impact on the baseline skin tone determined by genetics.
Conclusion
Exploring skin tone, skin shades, and the role of genes reveals the incredible diversity and beauty within the human population. From fair to dark, each skin shade holds its unique characteristics and cultural significance. While genetics plays a fundamental role in determining skin tone, other factors like sun exposure and environmental influences also shape our complexion. Understanding and appreciating the diversity of skin shades can foster inclusivity and promote a broader acceptance of different appearances.